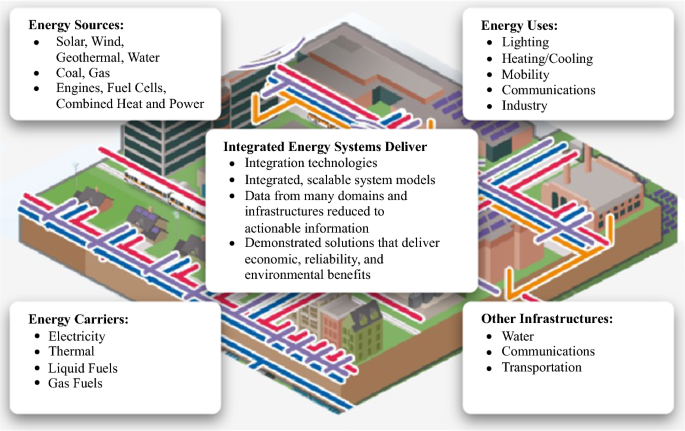
Introduction:
The pursuit of sustainable energy solutions has led to the concept of Environmental Energy Integration, a holistic approach to harnessing and combining various environmentally friendly energy sources. This article explores the significance of environmental energy integration and its role in achieving sustainable and efficient energy systems. To delve deeper into this innovative approach, visit Environmental Energy Integration.
Diverse Energy Sources:
One of the key aspects of Environmental Energy Integration is the incorporation of diverse energy sources. This includes renewable resources such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy. By leveraging a mix of these sources, systems can capitalize on the strengths of each, providing a more consistent and reliable energy supply. This diversity is crucial for overcoming the intermittency associated with individual renewable sources.
Smart Grids and Energy Storage:
Environmental Energy Integration often involves the implementation of smart grids and advanced energy storage systems. Smart grids enable real-time monitoring and optimization of energy distribution, ensuring that energy is efficiently directed where it is needed. Energy storage technologies, such as advanced batteries, contribute to smoothing out fluctuations in energy production and consumption, enhancing overall system stability.
Optimizing Energy Efficiency:
Efficiency is a central theme in Environmental Energy Integration. Systems are designed to optimize energy efficiency at every stage, from generation to consumption. This involves using advanced technologies, implementing energy-efficient practices, and prioritizing the reduction of energy wastage. The goal is to extract maximum value from the energy produced while minimizing environmental impact.
Decentralized Energy Systems:
A notable characteristic of Environmental Energy Integration is the move towards decentralized energy systems. Rather than relying solely on large, centralized power plants, the integration approach involves distributed energy generation. This decentralization enhances resilience, reduces transmission losses, and allows communities to have more control over their energy sources.
Interconnected Microgrids:
Microgrids play a vital role in Environmental Energy Integration, offering localized energy generation and distribution. Interconnected microgrids create a networked system that enhances reliability and resilience. In the event of a disruption in one area, the interconnected nature allows for the seamless flow of energy from other microgrids, minimizing the impact of outages.
Technological Innovations:
The integration of environmental energy is closely tied to ongoing technological innovations. Advancements in sensors, automation, and artificial intelligence contribute to the intelligence of integrated systems. These technologies enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and adaptive control, ensuring that energy systems operate at peak efficiency.
Community Involvement and Education:
Successful Environmental Energy Integration requires community involvement and education. Communities play a crucial role in supporting and adopting integrated energy solutions. Education initiatives raise awareness about the benefits of environmental energy integration, encouraging individuals and businesses to actively participate in sustainable practices and reduce their carbon footprint.
Policy Support and Incentives:
Government policies and incentives are instrumental in driving Environmental Energy Integration. Supportive regulations, subsidies, and incentives can accelerate the adoption of integrated energy solutions. Policymakers play a critical role in creating an enabling environment that encourages investment in sustainable and integrated energy infrastructure.
Environmental Impact and Carbon Reduction:
A primary motivation for Environmental Energy Integration is its positive impact on the environment. By transitioning to a system that relies on renewable sources and emphasizes energy efficiency, carbon emissions can be significantly reduced. This contributes to the global effort to mitigate climate change and create a more sustainable future.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Environmental Energy Integration represents a forward-thinking and comprehensive approach to energy management. To explore more about this innovative concept, visit Environmental Energy Integration. By embracing diverse energy sources, optimizing efficiency, and leveraging technological advancements, integrated energy systems pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient energy future.


