Navigating Economic Waters: United States Fiscal Policy
In the intricate world of economics, the fiscal policy of the United States stands as a guiding force. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of the country’s fiscal landscape, exploring economic trends, policy decisions, and the factors shaping the nation’s financial trajectory.
Historical Foundations: Tracing the Roots of Fiscal Policy
Understanding the present requires a journey into the past. The fiscal policy of the United States has evolved over centuries, shaped by historical events, economic philosophies, and the changing needs of society. Tracing these historical foundations provides a context for analyzing the current fiscal landscape.
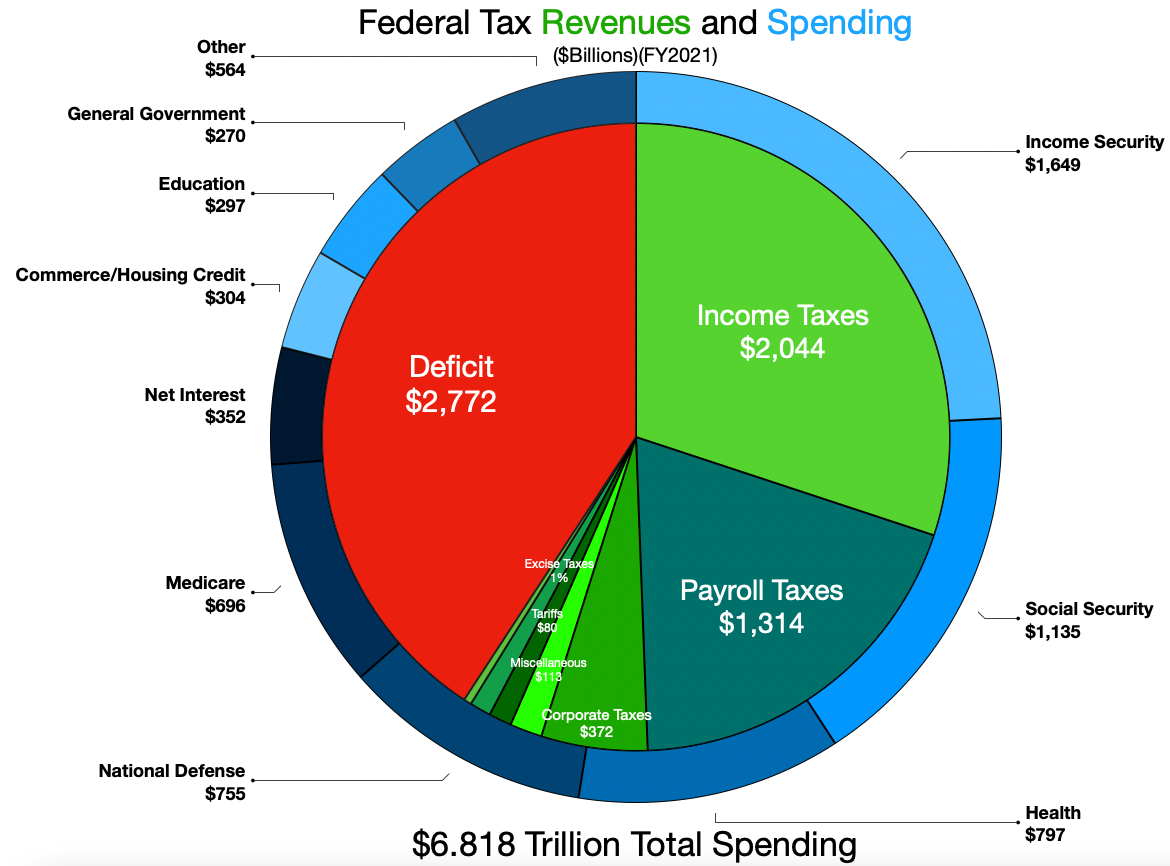
Government Revenue and Expenditure: A Delicate Balance
At the heart of the U.S. fiscal policy is the intricate dance between government revenue and expenditure. Tax policies, federal spending, and budget allocations are integral components that influence economic stability. Analyzing the delicate balance between income and spending sheds light on the nation’s fiscal health.
Economic Indicators: Gauging the Pulse of the Nation
Key economic indicators serve as vital signs, reflecting the health of the nation’s economy. Metrics like GDP growth, unemployment rates, inflation, and trade balances provide a comprehensive view. Examining these indicators offers insights into the overall fiscal well-being and economic trajectory of the United States.
Government Budget: Blueprint for National Priorities
The annual government budget is a tangible representation of national priorities. It outlines where financial resources will be allocated, reflecting the government’s economic and social objectives. Delving into the budgetary decisions unveils the nation’s focus, be it infrastructure investment, social programs, or deficit reduction.
Monetary Policy: The Federal Reserve’s Role
Guiding the nation’s fiscal policy is the crucial role of the Federal Reserve and its monetary policy. Interest rates, money supply management, and regulatory measures are employed to achieve economic objectives. Understanding the Federal Reserve’s strategies provides insights into the overall fiscal direction of the United States.
Global Interactions: The U.S. in the International Economic Arena
The United States does not exist in isolation; global economic interactions play a significant role in shaping its fiscal policy. Trade relationships, geopolitical considerations, and international economic trends impact the nation’s financial landscape. Analyzing these global interactions offers a holistic view of the challenges and opportunities faced by the U.S.
Social Programs and Fiscal Responsibility: Striking a Balance
An essential aspect of U.S. fiscal policy is the interplay between social programs and fiscal responsibility. Balancing the needs of the population with prudent financial management is an ongoing challenge. Examining policies related to healthcare, education, and social services provides insights into the nation’s commitment to societal well-being.
Debt Management: Addressing Financial Obligations
The management of national debt is a constant consideration in U.S. fiscal policy. Striking a balance between investing in the nation’s future and managing financial obligations requires strategic planning. Analyzing approaches to debt management unveils the government’s philosophy in handling financial responsibilities.
Future Outlook: Navigating Economic Uncertainties
As the United States faces a future marked by technological advancements, demographic shifts, and global economic dynamics, predicting the fiscal trajectory becomes complex. Assessing policy initiatives, economic resilience, and sustainability measures provides a glimpse into the nation’s preparedness for the uncertainties that lie ahead.
United States Fiscal Policy Insights for Informed Citizenship
For a more in-depth exploration of the United States fiscal policy, visit keozanara.my.id. Armed with insights into economic trends, historical context, and policy decisions, citizens can actively engage in discussions about the nation’s fiscal future, contributing to informed and participatory governance.


